Difference between revisions of "MIA electric"
(→MIA >> Monitor = MIAtor) |
(→MIA >> Monitor = MIAtor) |
||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
LCDline[1] = "MIA>>Monitor=MIAtor"; | LCDline[1] = "MIA>>Monitor=MIAtor"; | ||
LCDline[2] = "bastelbude.grade.de"; | LCDline[2] = "bastelbude.grade.de"; | ||
| − | LCDline[3] = " ver. 2017-12- | + | LCDline[3] = " ver. 2017-12-21"; |
Serial.begin(115200); | Serial.begin(115200); | ||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
Volts = ((float)(rxBuf[2]*256+rxBuf[3]))/100; // Voltage with decimals | Volts = ((float)(rxBuf[2]*256+rxBuf[3]))/100; // Voltage with decimals | ||
Amps = ((float)(rxBuf[0]*256+rxBuf[1]))/10; // current drawn or regenerated, allow negative | Amps = ((float)(rxBuf[0]*256+rxBuf[1]))/10; // current drawn or regenerated, allow negative | ||
| − | Celsius = ((float)rxBuf[4] | + | Celsius = ((float)rxBuf[4]); // Temperature, allow negative |
SOC = ((int)rxBuf[5]); // State Of Charge | SOC = ((int)rxBuf[5]); // State Of Charge | ||
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | SOH = ((int)rxBuf[7]); // State Of | + | SOH = ((int)rxBuf[7]); // State Of Health |
| − | |||
LCDline[1] = Status; //set second line | LCDline[1] = Status; //set second line | ||
LCDline[1] += Emergency; | LCDline[1] += Emergency; | ||
Revision as of 16:41, 21 December 2017
Contents
sandbox
CAN-bus sniffing
- parts
- Arduino UNO R3 (or CH340 clone EUR 6,49)
- MCP2515 / TJA1050 shield
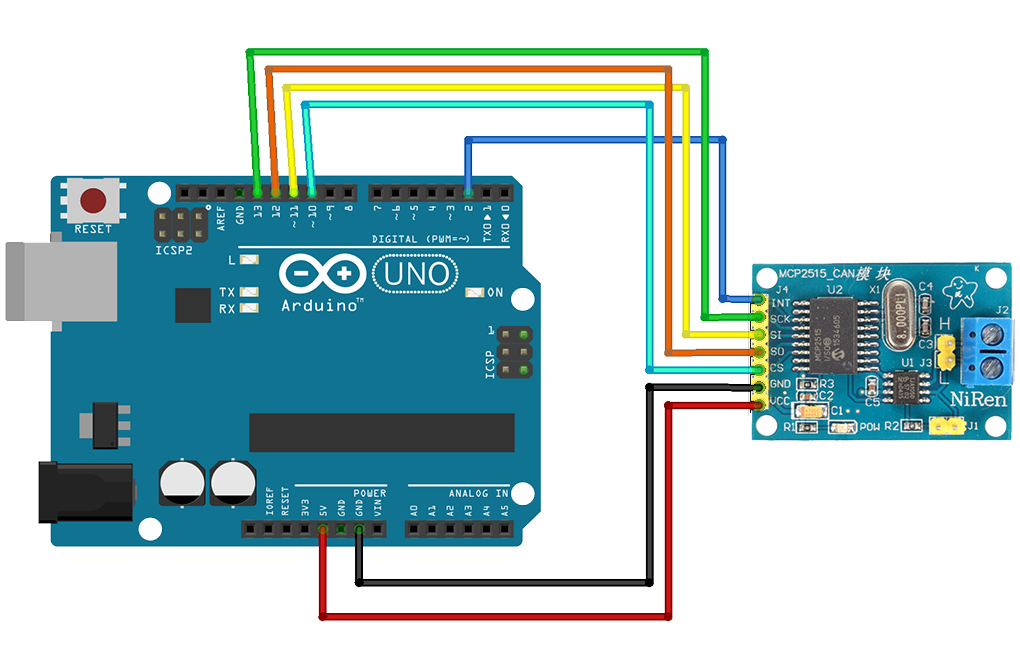 (8MHz EUR 4,79)
(8MHz EUR 4,79) - https://github.com/latonita/arduino-canbus-monitor (MCP_8MHz, CAN_500KBPS)
- OBD-II connector: Pin-6=CAN-high / Pin-14=CAN-low EUR 1,69
- CANcool https://github.com/MHS-Elektronik/CANcool
CANcool
'Berechnungs-Term'
- operators:
+ // addition - // subtraction * // multiplication / // division << // Bit shift left >> // Bit shift right & // AND | // OR ~ // XOR
- variables:
d0 1st byte (decimal) d1 2nd byte (decimal) d3 3rd byte (decimal) d4 ... d5 ... d6 ... d7 ...
- samples:
d0 // unsigned char (8-bit) (d0 - ((d0 >> 7)*256)) // signed char (8-bit) Two's complement ((d0 << 8) + d1) ^= MSB * 256 + LSB // unsigned short (16-bit) (((d0 << 8) + d1) - ((d0 >> 7)*65536)) // signed short (16-bit) Two's complement ((d0 << 24) + (d1 << 16) + (d2 << 8) + d3) // unsigned integer (32-bit) ((d0 << 24) + (d1 << 16) + (d2 << 8) + d3)-((d0 >> 7)*4294967296)) // signed integer (32-bit) Two's complement 256 = (1 << 8) 65536 = (1 << 16) 16777216 = (1 << 24) 4294967296 = (1 << 32)
MIA >> Monitor = MIAtor
- parts:
- Arduino UNO R3 (or CH340 clone EUR 6,49)
- MCP2515 / TJA1050 shield
 (8MHz EUR 4,79)
(8MHz EUR 4,79) - OBD-II connector: Pin-6=CAN-high / Pin-14=CAN-low EUR 1,69
- 20x4 LCD display plus I2C EUR 8,77
- libaries:
- https://github.com/marcoschwartz/LiquidCrystal_I2C
- https://github.com/coryjfowler/MCP_CAN_lib (clockset to MCP_8MHz at mcp_can.h line 98)
- code:
- based on work of Voltix @ https://miahammia.wordpress.com/2017/10/08/infobox/
// MIA >> Monitor = MIAtor
// all about @ https://bastelbude.grade.de/mediawiki/index.php?title=MIA_electric#MIA_.3E.3E_Monitor_.3D_MIAtor
// based on Voltix's work @ https://miahammia.wordpress.com/2017/10/08/infobox/
// CANbus
#include <mcp_can.h> // https://github.com/coryjfowler/MCP_CAN_lib (clockset to MCP_8MHz at mcp_can.h line 98)
#include <SPI.h>
// LCD
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // https://github.com/marcoschwartz/LiquidCrystal_I2C
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x3F,20,4); // set the LCD address to 0x3F for a 20 chars and 4 line display
long unsigned int rxId;
unsigned char len = 0;
unsigned char rxBuf[8];
float Volts;
float Amps;
float Celsius;
int SOC;
int SOH;
String Status;
String Emergency;
String Regeneration;
float ChargeCurrent;
float ChargeVoltage;
char myBuf[8];
String LCDline[4];
MCP_CAN CAN0(10); // Set CS to pin 10
void myPrint(){
Serial.println(LCDline[0]);
Serial.println(LCDline[1]);
Serial.println(LCDline[2]);
Serial.println(LCDline[3]);
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print(LCDline[0]);
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print(LCDline[1]);
lcd.setCursor(0,2);
lcd.print(LCDline[2]);
lcd.setCursor(0,3);
lcd.print(LCDline[3]);
delay(1000); // 1 second
}
void setup()
{
lcd.init(); // initialize the lcd
lcd.init();
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.backlight();
LCDline[0] = " Hello world!";
LCDline[1] = "MIA>>Monitor=MIAtor";
LCDline[2] = "bastelbude.grade.de";
LCDline[3] = " ver. 2017-12-21";
Serial.begin(115200);
CAN0.begin(CAN_500KBPS); // init can bus : baudrate = 500k
pinMode(2, INPUT); // Setting pin 2 for /INT input
Serial.println("MCP2515 Library Receive Example...");
//myPrint();
}
void loop()
{
if(!digitalRead(2)) // If pin 2 is low, read receive buffer
{
CAN0.readMsgBuf(&len, rxBuf); // Read data: len = data length, rxBuf = data byte(s)
rxId = CAN0.getCanId(); // Get message ID
if (rxId == 0x620) // battery related messageID 620
{
LCDline[0] = "Bat: ";
Volts = ((float)(rxBuf[2]*256+rxBuf[3]))/100; // Voltage with decimals
Amps = ((float)(rxBuf[0]*256+rxBuf[1]))/10; // current drawn or regenerated, allow negative
Celsius = ((float)rxBuf[4]); // Temperature, allow negative
SOC = ((int)rxBuf[5]); // State Of Charge
LCDline[0] = dtostrf(Volts,4,1,myBuf); //set first line
LCDline[0] += "V | ";
LCDline[0] += dtostrf(Amps,6,1,myBuf); //length of string=6 decimal places=1
LCDline[0] += "A |";
LCDline[0] += dtostrf(Celsius,2,0,myBuf); //length of string=2 decimal places=0
LCDline[0] += "C";
switch (rxBuf[6]&0x07) { //mask lowest 3 bits (48+49+50) = status
case 0:
Status = "Ready | ";
break;
case 1:
Status = "Run | ";
break;
case 2:
Status = "Downgrad | ";
break;
case 3:
Status = "Charge | ";
break;
case 4:
Status = "Error | ";
break;
case 5:
Status = "Init | ";
break;
case 6:
Status = "Stop | ";
break;
}
if ((rxBuf[6]&0x40)== 0) // bit 54 Emergency
{
Emergency = "noEmerg";
} else {
Emergency = "Emergency";
}
if ((rxBuf[6]>>7)== 1) // bit 55 Regeneration
{
Regeneration = "Regen | ";
} else {
Regeneration = "noRegen | ";
}
SOH = ((int)rxBuf[7]); // State Of Health
LCDline[1] = Status; //set second line
LCDline[1] += Emergency;
LCDline[2] = Regeneration; // set third line
LCDline[2] += "H=";
LCDline[2] += SOH;
LCDline[2] += " C=";
LCDline[2] += SOC;
LCDline[2] += "%";
Serial.println(); // new line
Serial.print("ID 620 raw data: ");
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++) // Print each byte of the data
{
if(rxBuf[i] < 0x10) // If data byte is less than 0x10, add a leading zero
{
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(rxBuf[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
LCDline[3] = ""; // set fourth line
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++) // Print each byte of the data
{
if(rxBuf[i] < 0x10) // If data byte is less than 0x10, add a leading zero
{
LCDline[3] += "0";
}
sprintf(myBuf,"%hhX",rxBuf[i]);
LCDline[3] += myBuf;
}
myPrint(); // lcd-print and serial-print of all four lines
}
if (rxId == 0x621) // BMS error messageID 621
{
Serial.print("ID 621 raw data: ");
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++) // Print each byte of the data
{
if(rxBuf[i] < 0x10) // If data byte is less than 0x10, add a leading zero
{
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(rxBuf[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
}
if (rxId == 0x622) // BMS > Charger messageID 622
{
ChargeCurrent = ((float)(rxBuf[0]*256+rxBuf[1]))/10; // Amps with decimals
ChargeVoltage = ((float)(rxBuf[3]*256+rxBuf[4]))/100; // Voltage with decimals
Serial.print("ID 622 raw data: ");
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++) // Print each byte of the data
{
if(rxBuf[i] < 0x10) // If data byte is less than 0x10, add a leading zero
{
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(rxBuf[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
}
}
}
DC charging
CCS
- prerequisites
- explore V2G protocol
- discover BMS <> Charger CANbus conversation
- BMS/Battery e4v.eu
- onboard charger ies-synergy.com
- develop BMS <> PCL communication
- parts
- CCS-socket e.g. Phoenix Contact ~EUR 800,-
- input voltage monitor
- power contactor (+125A disconnecting device) Tyco ~EUR 150,-
- current monitor
- V2G in-vehicle-charge-controller e.g. EVAcharge SE ~EUR 750,-
- ARM microcontroller
- Linux OS
- fully programmable
- PWM duty cycle detection (CP low level communication)
- switchable resistors (CP low level communication)
- HomePlug Green PHY integration (PLC high level communication)
- Proximity pilot signal input (PP)
- lock-motor output
- lock-motor end switch input
- lock-motor fault pin
- CAN transceiver (BMS communication)
- 6 GPIOs (current-monitoring?, voltage-monitoring?, temprature-monitoring?, power contactor-driver?, (contactor-monitoring?))